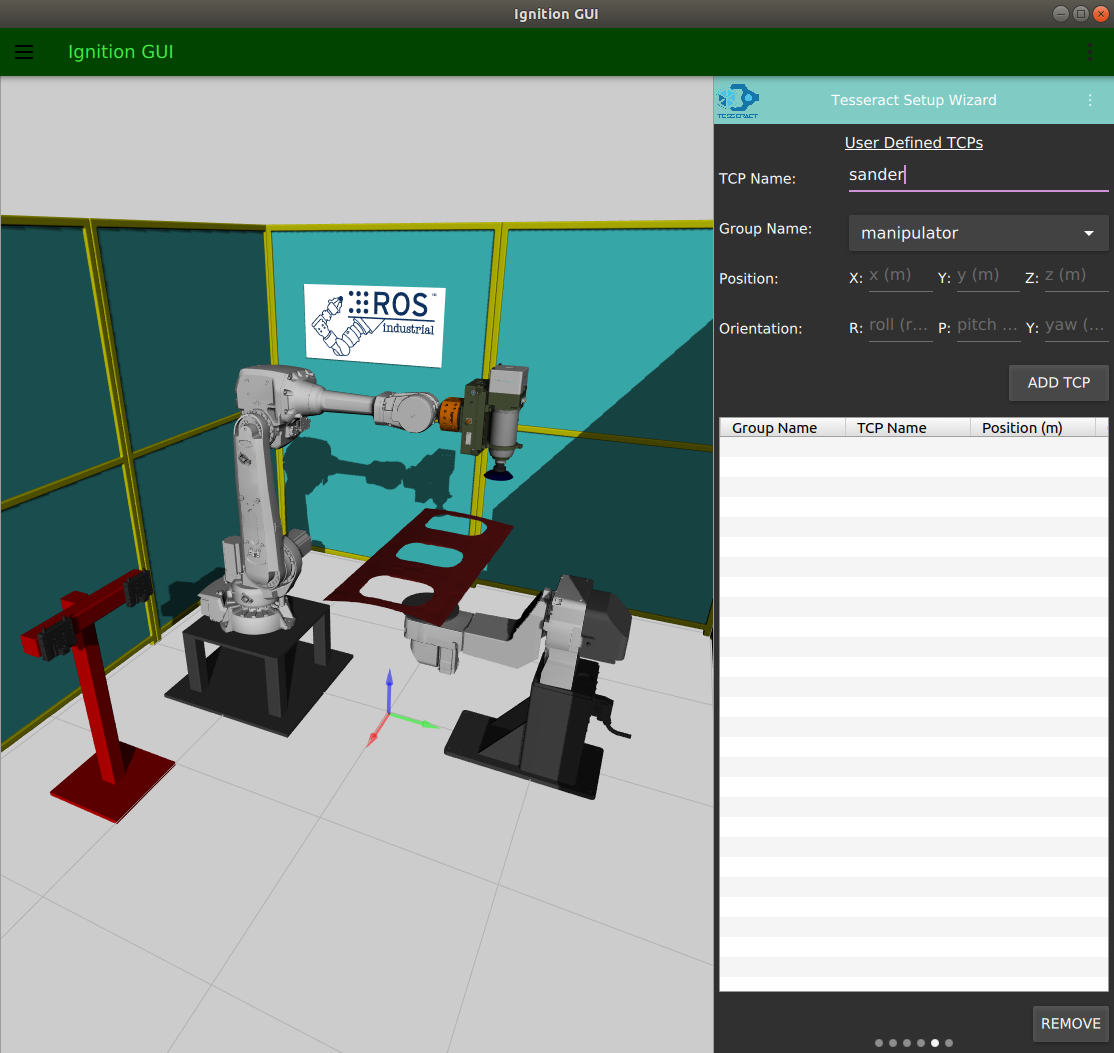
Tesseract Setup Wizard Leveraging Ignition
/Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is excited to announce that it has adopted Ignition Robotics Software as the visualization tool set for the Tesseract Motion Planning Framework. Ignition Robotics Software provides a modular set of libraries related to rendering, GUI, math, physics and much more.
Over the past few years SwRI has received several inquires related to richer visualization, simulation and ease of use tools for industrial automation applications allowing a user without programming experience to perform tasks that leverage the advanced capabilities provided by ROS. The goal was to first start with something simple that would add value to the open-source community. It was chosen to start by developing a setup wizard for the Tesseract Motion Planning Framework, further down more details are provided.
If you are familiar with the current tools within ROS you may be asking yourself why we chose to leverage Ignition Robotics Software over something like RViz, RobotWeb Tools, etc. In my opinion, the Ignition Robotics Software is more user-experience focused and the others are more developer focused, for a specific platform. The Ignition GUI leverages Qt Quick, which provides several advantages over the legacy Qt Widgets. These advantages allow it not only to be used on a desktop but also on tablets and smart phones, along with multiple methods for web deployment; opening up the possibility to leverage this tool similar to how you would use an Industrial Human Machine Interface (HMI). In addition, Qt Quick allows for a cleaner solution for separating the UI development from the business logic, allowing faster development and integration.
Another aspect of the Ignition Robotics Software is the rendering capabilities which provides not only Ogre, but Ogre2 and OptiX. And because of its plugin architecture it will most likely see more support for other rendering libraries in the future. Lastly, an additional advantage is having direct access to physics provided by Ignition Physics for simulating various industrial processes like sanding, grinding and painting in the future.
The other component of this exercise was to determine how to deploy the User Tools. Since we are talking about deploying applications instead of libraries which are mostly self contained, it was key to utilize a method of deployment that allows these tools to be easily accessed by the user, with frequent improvements and support for early access to enable testing before making new features available. For this we have chosen to leverage Snapcraft and the Snap Store, provided by Canonical, for deploying these user based tools on Linux and we are currently investigating using MSIx for deployment on Windows.
Before I move on to providing details on Tesseract Ignition, I would like to recognize two key individuals instrumental throughout the development and decision process. I would like to recognize Louise Poubel, from Open Robotics, for her support related to the Ignition Robotics Software packages, and Kyle Fazzari, from Canonical, for his support related to building and deploying this tool to the Snap Store. Thank you both for your time and guidance on this effort and I look forward to further collaboration.
Tesseract Ignition Overview: This package provides two applications, the first is the Tesseract Setup Wizard and second is Tesseract Visualization outlined below and can be downloaded on the Snap Store by clicking on the Snap Store button below. Please see our video for a walk through of these tools and how you may start leveraging it now.
- Tesseract Setup Wizard
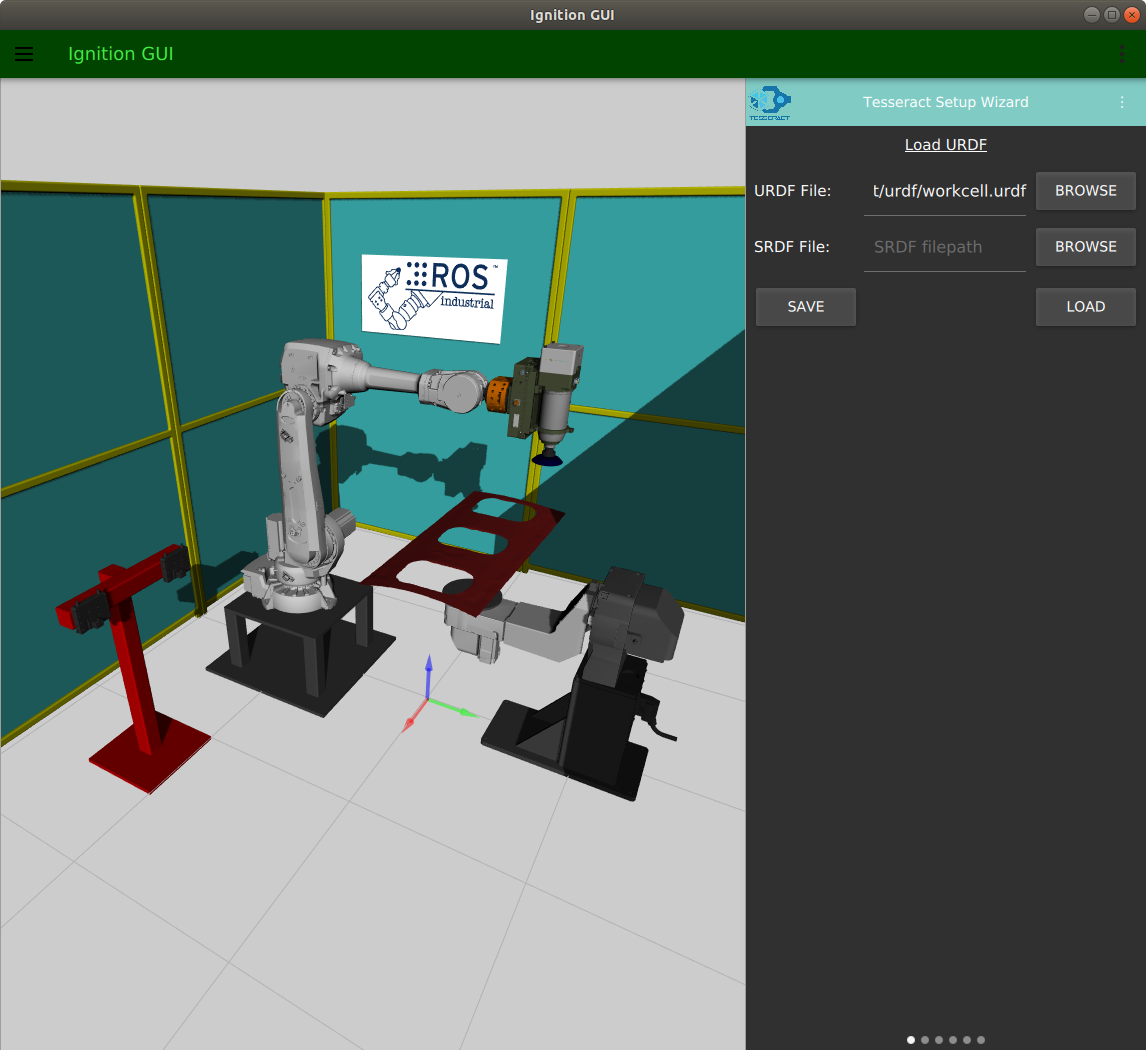
- Loading a URDF and SRDF
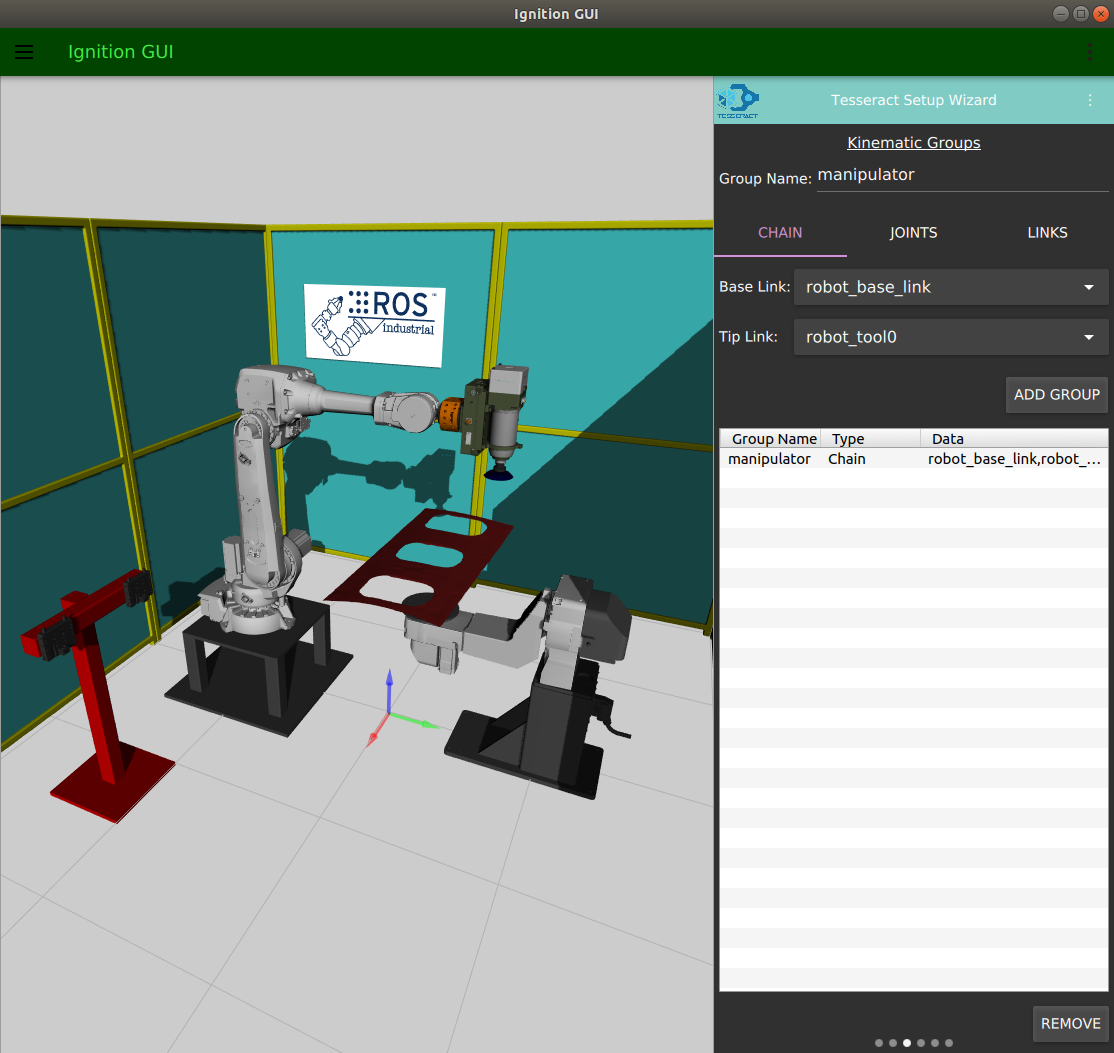
- Defining kinematic groups
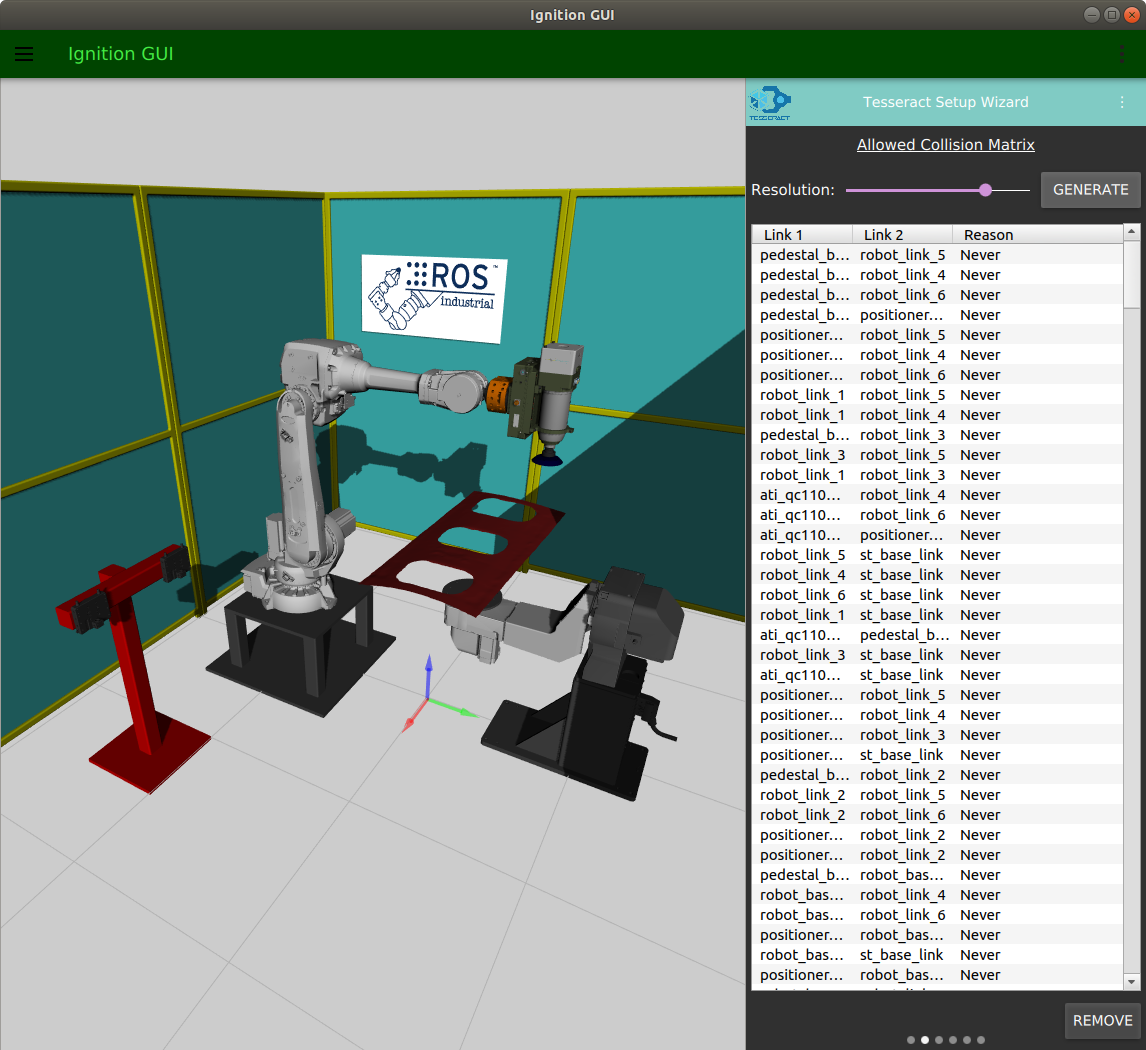
- Defining allowed collision matrix
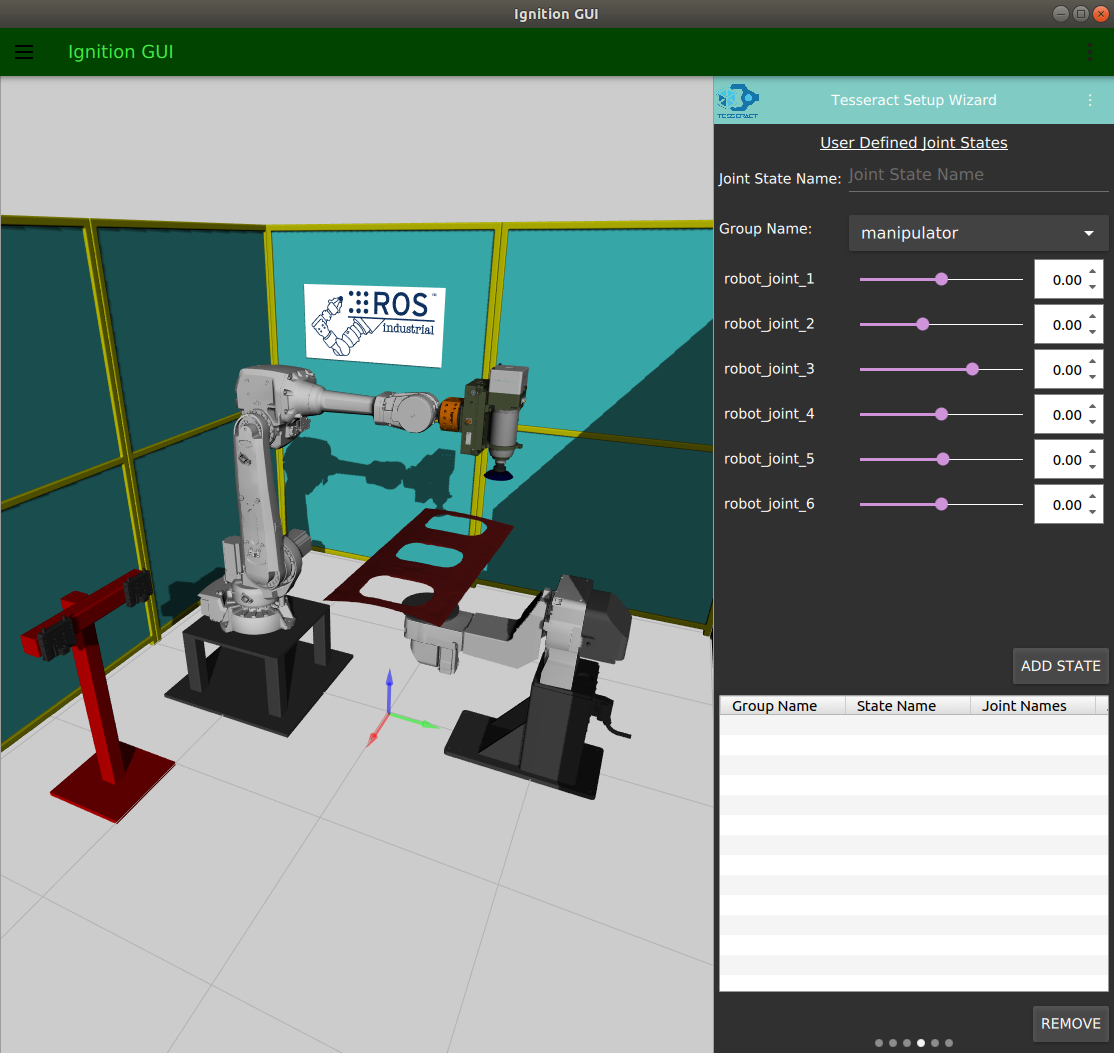
- Defining group states
- Defining group tool center points
- Defining group opw kinematics parameters
- Saving SRDF
- Tesseract Visualization
- Trajectory Simulation
- Tool Path Visualization
- Marker Visualization